Understanding Thoracic Spine Disorder: Insights and Solutions
The thoracic spine disorder is a pressing issue affecting many individuals globally. This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of thoracic spine disorders, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and effective treatment options. Additionally, we will explore ways to prevent these disorders and discuss their impact on overall health.
What is Thoracic Spine Disorder?
The thoracic spine, consisting of 12 vertebrae located in the upper and mid-back, plays a crucial role in supporting the rib cage and protecting vital organs. A thoracic spine disorder refers to any dysfunction that affects this region, leading to pain and mobility issues. Conditions can vary from minor strains to severe degenerative diseases.
Causes of Thoracic Spine Disorder
Understanding the causes is vital for effective treatment. The following are common causes of thoracic spine disorder:
- Injury: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can lead to trauma in the thoracic region.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Aging can lead to the wear and tear of intervertebral discs, resulting in pain.
- Posture: Poor posture, especially during long hours of sitting, can contribute significantly.
- Osteoarthritis: This condition involves the degeneration of joints and can affect the thoracic spine as well.
- Herniated Discs: Discs can bulge or rupture, pressing against nerves and causing pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: The narrowing of the spinal canal can lead to nerve compression and pain.
Symptoms of Thoracic Spine Disorder
Recognizing the symptoms of a thoracic spine disorder is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Often felt in the mid-back area, which may exacerbate during certain activities or movements.
- Nerve Pain: Tingling, numbness, or sharp pain radiating to the arms or legs.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty in performing everyday tasks due to muscle fatigue.
- Postural Distortions: Visible changes in posture, such as rounded shoulders or stooped back.
- Decreased Mobility: Limited range of motion in the upper body due to pain or stiffness.
Diagnosis of Thoracic Spine Disorder
Accurate diagnosis is the first step towards effective management. A healthcare provider may utilize the following methods:
1. Physical Examination
The physician will perform a thorough physical examination to assess posture, range of motion, and areas of discomfort.
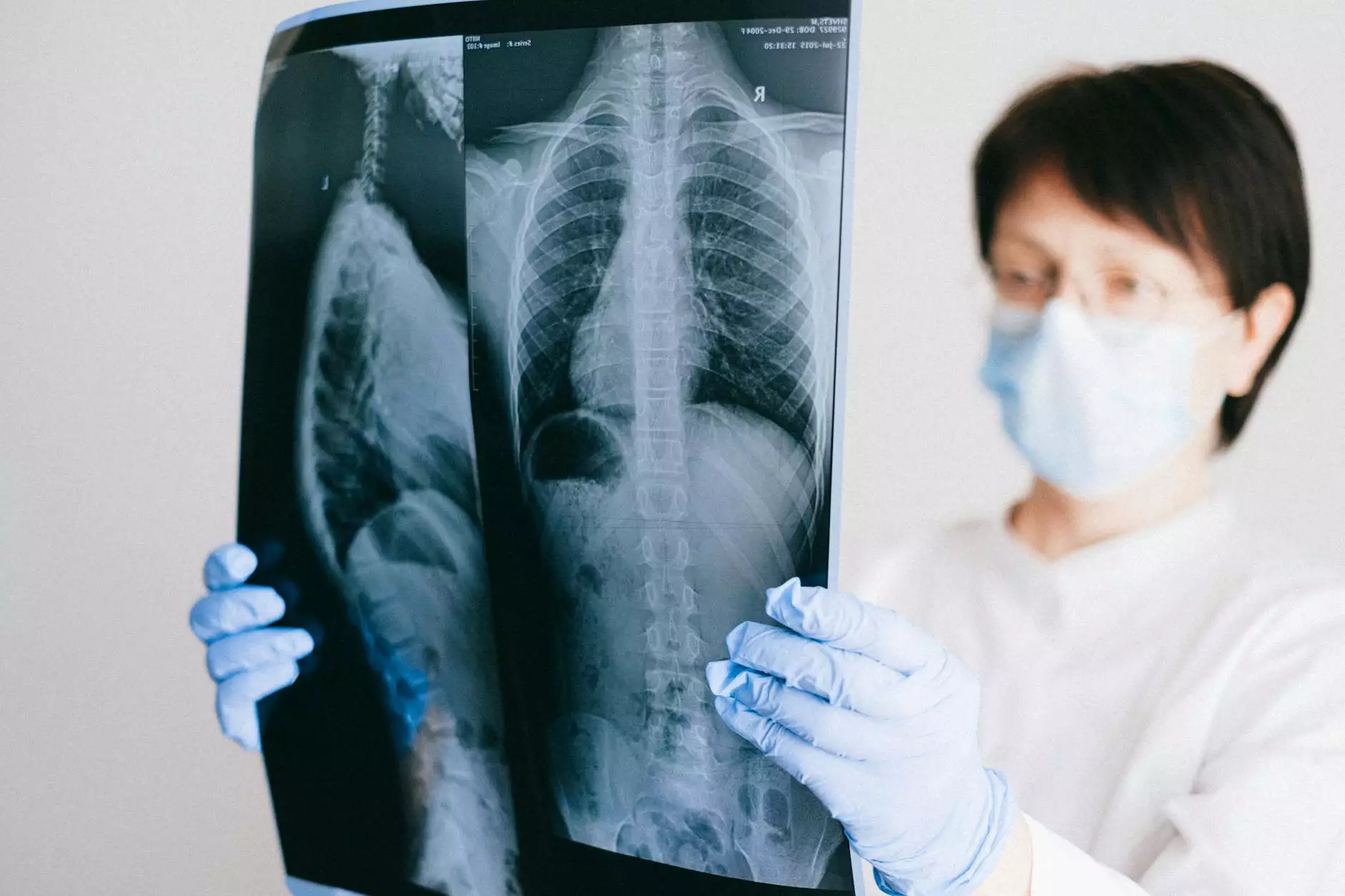
2. Imaging Tests
X-rays, CT scans, and MRI are commonly used to visualize the thoracic spine and identify structural issues.
3. Neurological Evaluation
This involves assessing reflexes, sensation, and muscle strength to determine any nerve involvement.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Spine Disorder
Once diagnosed, various treatment options are available for managing thoracic spine disorders:
1. Conservative Treatments
Most cases can be managed with non-invasive treatments, including:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relief like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can alleviate discomfort.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can help in restoring proper alignment and function.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Alternating between hot and cold compresses can help reduce inflammation and pain.
2. Medical Treatments
In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, medical interventions may be necessary:
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can be injected directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation.
- Prescription Medications: Muscle relaxants or stronger pain medications may be prescribed.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and massage therapy can aid in pain relief.
3. Surgical Treatments
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required. Common surgical procedures include:
- Discectomy: Removing a herniated disc that is pressing on nerves.
- Laminectomy: Removing part of the vertebra to relieve pressure on the spinal cord.
- Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
Preventing Thoracic Spine Disorders
While not all thoracic spine disorders can be prevented, certain measures can significantly reduce the risk:
1. Maintaining Good Posture
Keeping an ergonomic posture while sitting and standing can help align the spine correctly. Consider using ergonomic chairs and workstations.
2. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the back muscles and promotes flexibility. Incorporate exercises that target the core, back, and shoulders.
3. Proper Lifting Techniques
Always lift heavy objects using the legs, not the back, to prevent injury. Keep the load close to the body and avoid twisting.
4. Adequate Rest and Sleep
Ensure your sleeping position supports spinal alignment. Use appropriate mattresses and pillows to keep the spine aligned during sleep.
The Impact of Thoracic Spine Disorder on Overall Health
A thoracic spine disorder can significantly affect various aspects of health, particularly physical and mental well-being:
1. Physical Limitations
The pain and discomfort associated with thoracic spine disorders can lead to decreased mobility, making it challenging to engage in daily activities or exercise.
2. Mental Health
Chronic pain can take a toll on mental health, leading to issues such as anxiety and depression. Seeking psychological support can be beneficial.
3. Quality of Life
Overall quality of life can diminish due to persistent pain, loss of mobility, and psychological distress. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can restore functionality.
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent pain or other symptoms related to thoracic spine disorder, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the disorder and lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of thoracic spine disorders empowers individuals to take charge of their health. Through education, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, it is possible to relieve pain and enhance quality of life. Maintain good posture, engage in regular physical activity, and seek professional help when necessary to protect your thoracic spine health.
Additional Resources
For more information, consider visiting IAOM-US, where you can find valuable insights into health, medical education, and chiropractic care.



